CONSTRUCTION REGULATIONS FOR ACCEPTANCE OF CONCRETE WORK
Materials for concrete production must ensure technical requirements according to current standards, and at the same time meet additional requirements of design work.
During storage, transportation and production of concrete, materials must be preserved, avoiding contamination or mixing of grain sizes and types. When encountering the above cases, immediate remedial measures must be taken to ensure quality stability.
Materials that do not fully comply with the standards or are not mentioned in this standard, should only be used for concrete production, if there is sufficient scientific and technological evidence (through confirmation by a qualified testing facility) and with the consent of the investor.
1. What are the standards for qualified materials?
1.1. Cement
The cement used must satisfy the regulations of the following standards:
- Portland cement TCVN 2682: 1985.
- Portland Pufzolan cement TCVN 4033: 1985. Portland cement - blast furnace slag TCVN 4316: 1986.
- Special types of cement such as sulfate-resistant cement, low-heat cement, etc., must be used according to design instructions.
The type and grade of cement used must be suitable for the design and conditions, properties, and working environment characteristics of the structure.
The use of imported cement must have a technical certificate from the country of manufacture. When necessary, testing must be performed to determine the quality according to current Vietnamese standards.
In-situ cement testing must be carried out in the following cases:
- When designing concrete components;
- There is doubt about the quality of cement;
- The cement batch has been stored for more than 3 months since the date of production.
The transportation and storage of cement must comply with the standard TCVN 2682; 1992 “Portland cement”.
>>> See more:
- Hướng dẫn cách kiểm tra chất lượng xi măng hiệu quả nhất
- Làm thế nào để mua vật liệu xây dựng khi chưa biết gì?
1.2. Sand
Sand used for making heavy concrete must satisfy the requirements of TCVN 1770: 1986 “Construction sand – Technical requirements”.
Note: For sand with small grains (modulus of magnitude less than 2), when used, it is necessary to comply with TCVN 127: 1986 “Fine sand for making concrete and mortar”.
- Sand quality testing is conducted according to standards from TCVN 337: 1986 to TCVN 346: 1986 “Construction sand – testing methods”.
- If using sand from coastal areas or open water areas, it is necessary to check the content of Cl- and SO-. If using mine sand or hill sand, it is necessary to check the content of amorphous silica.
The sand storage area must be dry, piled in groups of grains according to the level of cleanliness and dirt for ease of use and must have measures to prevent wind, rain, drift and impurities.
1.3. Large aggregates
Large aggregates used for concrete include crushed stone crushed from natural stone, crushed gravel crushed from natural gravel. When using these types of large aggregates, the quality must be ensured according to the regulations of TCVN 1771: 1986 "Crushed stone, crushed gravel, gravel used in construction".
In addition to the requirements of TCVN 1771: 1986, crushed stone and gravel used for concrete must be divided into groups with grain sizes in accordance with the following regulations:
- For slabs, the largest grain size must not be larger than 1/2 of the slab thickness;
- For reinforced concrete structures, the largest grain size must not be larger than 3/4 of the smallest clear distance according to the cross-section of the structure;
- For construction works using sliding formwork, the largest grain size must not exceed 1/10 of the smallest edge size according to the cross-section of the structure;
- When using a concrete mixer with a volume greater than 0.8m3, the largest size of crushed stone and gravel shall not exceed 120mm. When using a mixer with a volume less than 0.8m2, the largest size shall not exceed 80mm;
- When transporting concrete by concrete pump, the largest particle size shall not be larger than 0.4 of the inner diameter of the pump nozzle for gravel and 0.33 for crushed stone;
- When pouring concrete by elephant trunk pipe, the largest particle size shall not be larger than 1/3 of the small part of the diameter.
1.4. Water
Water used for mixing and curing concrete must meet the requirements of TCVN 4506: 1987 “Water for concrete and mortar – Technical requirements”.
All drinking water sources can be used for mixing and curing concrete. Do not use wastewater from factories, dirty water from domestic drainage systems, muddy pond water, water mixed with grease to mix and cure concrete.
1.5. Additives
To save cement or improve the technical properties of concrete and concrete mixtures, suitable additives can be used in the concrete manufacturing process.
The use of additives must ensure:
- Creating a concrete mixture with properties suitable for construction technology;
- Not affecting the construction progress and not harming the requirements of future use of the project;
- Not affecting the corrosion of steel reinforcement.
The types of additives used must have technical certificates recognized by State management agencies. The use of additives must follow the instructions of the manufacturer.
1.6. Filler
Fillers in concrete must ensure that they do not affect the life of the concrete and do not corrode the steel.
When using fillers, they must be tested to have sufficient economic and technical basis, and must be approved by the design agency and the investor.
Note:
- Fillers are fine minerals that can be added to concrete to improve some properties of the concrete mixture.
- There are two types of fillers: inert fillers and active fillers (thermal ash ore slag powder, pozzolan powder, etc.).
2. Concrete work construction
2.1 Select concrete composition (required).
To ensure the quality of concrete, depending on the importance of each type of construction or each part of the construction, on the basis of the concrete grade regulations of the concrete component design, the following are selected:
- For concrete grade 100, the available calculation table in Appendix C can be used;
- For concrete grade 150 or higher, the material composition in the concrete must be designed through the laboratory (calculation and casting of test samples).
2.2 Concrete composition design
-
The design of concrete components is carried out by legally qualified testing facilities. When designing concrete components, the following principles must be ensured:
-
Use the correct materials to be used for construction;
-
The slump or hardness of the concrete mixture is determined depending on the nature of the project, the steel content, the method of transportation, and weather conditions. When selecting the slump of the concrete mixture for design, it is necessary to take into account the loss of slump during storage and transportation. The slump of the concrete mixture at the pouring location can be referred to in Table 11.
-

2.3 Field correction of concrete composition.
- The adjustment of concrete composition at the site is carried out according to the principle of not changing the N/X ratio of the designed concrete composition.
- When the aggregate is wet, it is necessary to reduce the amount of mixing water, keeping the required slump.
- When it is necessary to increase the slump of the concrete mixture to suit the construction conditions, water and cement can be added at the same time to keep the N/X ratio unchanged.
Depending on the scale and level of the project, determine the types of concrete test records according to the requirements of Table 19.
2.4 Concrete mix manufacturing
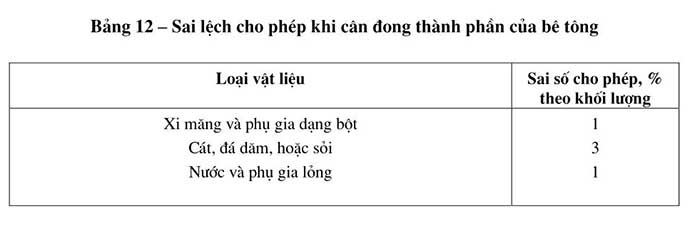
Cement, sand, crushed stone or gravel and liquid additives for making concrete mixture are weighed by mass. Water and additives are weighed by volume. The allowable error when weighing and measuring must not exceed the values shown in Table 12.
After washing, let the sand dry before weighing and measuring to reduce the amount of water in the sand.
The accuracy of the weighing and measuring equipment must be checked before each concrete pouring. During the weighing and measuring process, it is regularly monitored to detect and correct errors in time.
The concrete mixture must be mixed by machine. Only when the volume is small should it be mixed by hand.
Note: The amount of water added to concrete must include the amount of water in the admixture and the amount of water in the wet aggregate.
The sequence of pouring materials into the mixer must follow the following regulations:
- First pour 15% - 20% of the water, then pour cement and aggregate at the same time and gradually and continuously pour the remaining water;
- When using additives, mixing additives must be carried out according to the instructions of the additive manufacturer.
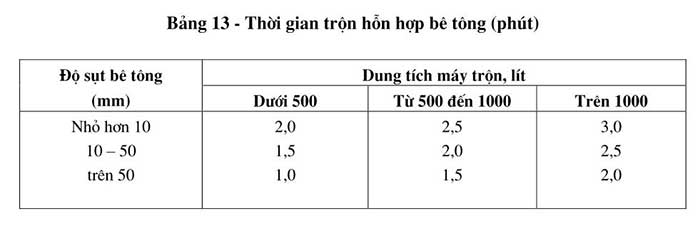
The mixing time of the concrete mixture is determined according to the technical characteristics of the equipment used for mixing. In the absence of precise technical parameters, the minimum time to mix a batch of concrete in the mixer can be taken according to the values listed in Table 13.
During the mixing process, to prevent the mixture from sticking to the mixing tank, every 2 working hours, pour all the large aggregates and water of a batch into the mixing tank and rotate the mixer for about 5 minutes, then add sand and cement to continue mixing according to the specified time.
If mixing concrete manually, the mixing floor must be hard enough, clean and not absorb water. Before mixing, the mixing floor must be moistened to prevent water absorption from the concrete mixture. The order of mixing the mixture manually is as follows: Mix the sand and cement thoroughly, then add and mix well into a dry mixture, finally add water and mix well until the mixture is uniform in color and has the specified slump.
2.5 Transporting concrete mixture.
The transportation of concrete mixture from the mixing place to the pouring place must ensure the following requirements:
- Use appropriate means of transportation to avoid the concrete mixture from being stratified, leaking cement water and losing water due to wind and sun.
- Use equipment, mixed manpower and means of transportation that must be arranged appropriately for the volume, speed of mixing, pouring and compacting concrete;
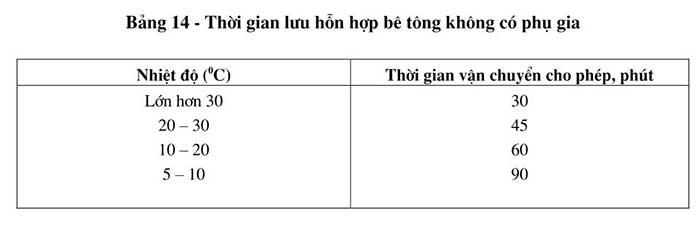
- The time allowed to keep the concrete mixture during transportation must be determined by experiment based on weather conditions, type of cement and type of additives used. If there are no experimental data, the values in Table 14 can be referred to.
Transporting concrete mixtures manually is only applicable for distances not exceeding 200m. If the concrete mixture is stratified, it must be mixed again before pouring into the formwork.
When using a hanging bucket to transport the concrete mixture, the concrete mixture poured into the hanging bucket must not exceed 90 - 95% of the bucket's capacity.
Transporting concrete mixtures by car or specialized equipment must ensure the following regulations and requirements:
- The thickness of the concrete layer in the truck bed must be greater than 40cm if using a dump truck;
- If transporting by specialized equipment that can be mixed while driving, the transportation technology is determined according to the technical parameters of the equipment used.
When using a concrete pump for transportation, the following requirements must be ensured:
- The composition and slump of the concrete mixture must be tested and pumped to ensure the quality of the concrete and construction conditions, and at the same time be suitable for the technical features of the pumping equipment.
- When constructing in hot weather, the outer surface of the pipe must be covered or painted white to limit solar radiation from heating the concrete.
When transporting concrete mixture by conveyor belt, the following requirements must be met:
- The working surface of the conveyor belt must be constructed in the form of a trough and use a rubber conveyor belt. Flat conveyor belts are only used when the length of the conveying line is less than 200m;
- The tilt angle of the conveyor belt must not exceed the values in Table 15. The conveyor belt surface must be inclined evenly, without sudden breaks;
- The conveying speed of the conveyor belt must not exceed 1m/s. The conveying speeds of the conveyor belts in the system must not differ by more than 0.1m/s;
- Pour concrete onto the conveyor belt through a funnel or trough so that the concrete mixture is spread evenly and continuously on the conveyor belt. The thickness of the concrete layer on the conveyor belt depends on the allowable load capacity of each type of conveyor belt;
- Concrete transferred from one conveyor belt to another or from the conveyor belt to the formwork must be done through a funnel to direct the concrete mixture to fall vertically.

2.6 Pouring and compacting in concrete work
Concrete pouring must ensure the following requirements:
- Do not distort the position of the steel reinforcement, the position of the formwork and the thickness of the concrete layer protecting the steel reinforcement.
- Do not use a rammer to move the concrete horizontally in the formwork;
- Concrete must be poured continuously until a structure is completed according to the design regulations.
To avoid stratification, the free fall height of the concrete mixture when pouring must not exceed 1.5m.
When pouring concrete with a free fall height greater than 1.5m, an inclined chute or an elephant trunk pipe must be used. If the fall height is greater than 10m, an elephant trunk pipe with a vibration device must be used.
When using an elephant trunk pipe, the pipe must be inclined from the vertical by no more than 0.25m per 1m of height, and in all cases, the bottom section of the pipe must be vertical.
When using an inclined chute, the chute must be closed and smooth. The width of the chute must not be less than 3 - 3.5 times the diameter of the largest aggregate particle. The slope of the chute must be ensured so that the concrete mixture does not get clogged or slide quickly, causing stratification. At the end of the chute, a vertical funnel must be placed to direct the concrete mixture to fall vertically to the pouring position and the cement mortar in the inclined chute must be regularly cleaned.
When pouring concrete, the following requirements must be met:
- Closely monitor the current status of formwork, scaffolding and reinforcement during construction to promptly handle any problems that may arise;
- The level of filling the formwork with concrete mixture must be consistent with the calculated data on the formwork's horizontal pressure resistance caused by the newly poured concrete mixture;
- In locations where the structure of the reinforcement and formwork does not allow for machine compaction, manually compaction must be used;
- When it rains, cover the concrete to prevent rainwater from falling on it. In case of stopping concrete pouring for more than the specified time (Table 18), wait until the concrete reaches 25 daN/cm2 before pouring concrete, and before pouring the concrete again, the surface must be treated to roughen it. Pouring concrete at night and in foggy conditions must ensure adequate lighting at the concrete mixing and pouring area.
The thickness of each concrete layer must be based on mixing capacity, transport distance, compaction capacity, structure properties and weather conditions, but must not exceed the values shown in Table 16.
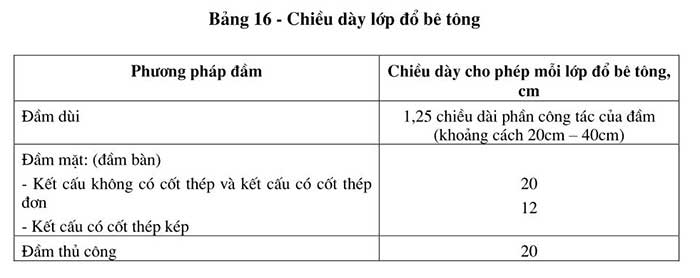
2.7 Pouring concrete
When pouring concrete for the foundation, it is necessary to ensure the regulations of Article 6.4.1. Foundation concrete must only be poured onto a clean cushion layer on hard ground.
>>> See more:
- Biện pháp đổ bê tông cột không bị rỗ
- Cần bao nhiêu cát, đá, xi măng cho một khối bê tông
- Quy trình đổ bê tông trong xây dựng nhà xưởng
Pour concrete columns and walls.
- Columns with a height of less than 5m and walls with a height of more than 3m should be poured continuously.
- Columns with a side size of less than 40cm; walls with a thickness of less than 15cm and columns with any cross-section but with overlapping steel belts should be poured concrete continuously in stages with a height of 1.5m.
- Columns higher than 5m and walls higher than 3m should be poured concrete in several stages; but the location and structure of the construction joints must be ensured to be reasonable.
Pouring concrete frame structure
-
Frame structures should be continuously poured with concrete; only when necessary should joints be constructed, but in accordance with the provisions of Article 6.6.4.
Pour concrete beams and slabs.
- When it is necessary to continuously pour concrete beams, monolithic slabs with columns or walls; first, finish pouring the columns or walls; then stop for 1 hour - 2 hours to allow the concrete enough time for initial shrinkage, then continue pouring concrete beams and slabs. In cases where it is not necessary to continuously pour concrete, the construction stop joints in columns and walls are placed 2cm - 3cm from the bottom surface of the beams and slabs.
- Pouring concrete beams (beams) and slabs must be carried out simultaneously. When beams, floors and similar structures are large in size (height greater than 80cm); each part can be poured separately but appropriate construction stop joints must be arranged; according to the provisions of Article 6.6.5.
Pouring concrete arch structure.
- Arch structures must be poured concrete simultaneously from both sides of the arch base to the top of the arch, not poured on the lower side or the higher side. If there is a construction stop joint, the plane of the stop joint must be perpendicular.
- Arches with an aperture of less than 10m should be poured concrete continuously from the base of the arch to the top of the arch.
- Arches with an aperture larger than 10m should have a stop joint every 2m - 3m perpendicular to the curved axis of the arch, 0.6m - 0.8m wide. These stop joints are filled with concrete with expanding additives after the previously poured concrete has shrunk.
Pouring concrete on the wall on which the vault of the tunnel wall is built must ensure the following regulations:
- The layers of concrete poured on the wall must be even and poured gradually until the height of 40c from the base of the vault is stopped; to allow the concrete time to shrink and then construct the vault.
- The concrete pouring part between the wall and the base of the vault must be treated to ensure the requirements according to the design regulations.
Pouring concrete on road surfaces, yards and airport runways must ensure the following requirements:
- Concrete must be poured continuously for the entire thickness of each concrete layer;
- Place expansion joints according to design regulations. If the design does not specify, expansion joints must be placed in two perpendicular directions, 4m - 6m apart; the width of the joint must be 1cm - 2cm and the height must be equal to the thickness of the structure;
- The stopping time between two layers must be appropriate.
Concrete dam.
Concrete compaction must ensure the following requirements:
- Different types of compactors can be used, but must ensure that after compaction, the concrete is compacted tightly and without holes.
- The compaction time at each location must ensure that the concrete is compacted thoroughly. The sign to recognize that the concrete has been compacted thoroughly is that the cement mortar floats to the surface and the air pockets are no longer present;
- When using a rammer, the rammer's movement should not exceed 1.5 times the rammer's effective radius; and it must be inserted 10cm deep into the previously poured concrete layer;
- When re-compacting the concrete, the appropriate time to compact is 1.5 hours - 2 hours after the first compaction. Re-compacting concrete is only suitable for structures with large surface areas such as roof floors, yards, car roads, etc. Do not re-compact large concrete blocks.
3. Concrete curing (mandatory)
After pouring, concrete must be maintained in conditions of humidity; and temperature necessary for curing and to prevent harmful effects; during the curing process of concrete.
Moisturizing
- Moisture curing is the process of keeping concrete with the necessary moisture; for setting and solidification after shaping. The method and process of moisture curing are implemented according to TCVN 5592: 1991 “Heavy concrete - natural moisture curing requirements)”.
- The required moisture curing time must not be less than the values listed in Table 17. During the curing period, the concrete must be protected against mechanical impacts; such as vibration, shock force, load and other potentially damaging impacts.
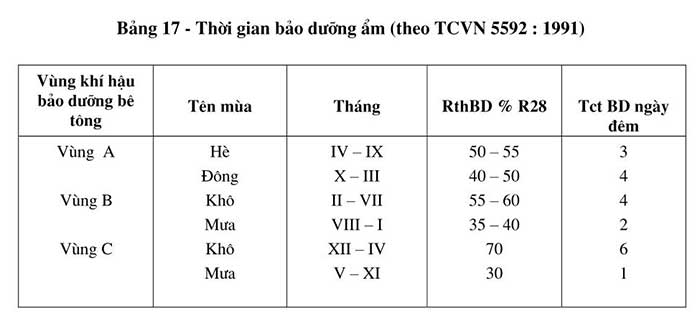
In which:
- Rth BD – Critical maintenance intensity;
- Tct BD – required maintenance time;
- Zone A (From Dien Chau to the North);
- Zone B (East of Truong Son and from Dien Chau to Thuan Hai);
- Zone C (Central Highlands and the South).
4. Circuit breakers
Construction joints must be located at locations where shear forces and bending moments are relatively small; and must be perpendicular to the direction of compression force transmission into the structure.
Horizontal construction stop circuit:
- Horizontal construction joints should be placed at the same height as the formwork.
- Before pouring new concrete, the old concrete surface must be treated, roughened, and moistened; and during pouring, it must be compacted so that the new concrete layer adheres firmly to the old concrete layer, ensuring the integrity of the structure.
The circuit stops vertically.
- The construction joints should be vertical or inclined; they should be constructed of steel mesh with mesh size of 5mm - 10mm and have a barrier.
- Before pouring a new layer of concrete, the old concrete surface should be moistened with water, roughened; cleaned and thoroughly compacted during pouring to ensure the integrity of the structure.
Concrete pouring work stop at column
The column stop circuit should be located in the following locations:
- On the top of the foundation;
- On the bottom of the beam, girder or under the crane girder support;
- On the top of the crane girder.
For large beams that are integral with the slab, the construction stop joint is arranged 2cm - 3cm from the bottom of the slab.
When pouring concrete for flat floors, the construction stop joint can be placed at any position but must be parallel to the shortest edge of the floor.
When pouring concrete on slabs with ribs in a direction parallel to the secondary beam, the construction stop joint is arranged within 1/3 of the middle section of the beam span.
When pouring concrete in a direction parallel to the main beam, the construction stop joint is arranged within the two middle sections of the beam span and the floor (each section is 1/4 of the span).
When pouring concrete for large-scale structures, arches, tanks, hydraulic works; bridges and complex parts of the project; the construction stop joint must be implemented according to the design regulations.
5. Roof waterproofing concrete construction work (mandatory application)
Roofs and floors with waterproof concrete layers must be constructed in accordance with the requirements of TCVN 5718: 1993 “Flat roofs and reinforced concrete floors in construction works – Waterproofing requirements”.
The thermal expansion joints of the waterproof concrete layer of the roof must be placed in two perpendicular directions. For roofs without a heat-resistant layer, the expansion joints must be placed 6m – 9m apart. For roofs with a heat-resistant layer that meets technical requirements; the distance between expansion joints must not exceed 18m.
5.1 Mass concrete construction work
Concrete and reinforced concrete structures are called large blocks when the smallest side dimension is not less than 2.5m and the thickness is greater than 0.8m.
When constructing large-block concrete, there are measures to limit thermal stress arising from the temperature difference between the outside and inside of the concrete block during the curing process.
Note: Temperature control measures must be implemented according to the design instructions. In cases where the design does not provide instructions, thermal stress can be reduced by the following measures:
Use plasticizers to reduce cement content;
- Use low-heat cement;
- Use retarding additives;
- Cool aggregates and mix concrete with low-temperature water;
- Install heat pipes from the inside of the concrete to the outside with cold water;
- Add more rock to the poured mass;
- Cover the concrete mass with insulation material to keep the temperature uniform in the concrete mass;
- Divide the poured mass appropriately to limit heat accumulation in the concrete mass. The division of the poured mass needs to be specifically determined taking into account the construction conditions; concrete materials, weather conditions and structural characteristics.
When constructing large-scale concrete works, the following regulations must be implemented:
- When dividing the structure into many blocks poured according to height; the contact surface between the poured blocks must be roughened to ensure the monolithic nature;
- The pouring of closed concrete blocks for filling blocks is carried out after the previously poured blocks have shrunk; and the temperature has decreased corresponding to the regulations in the construction organization design.
- For foundations subject to dynamic loads, concrete should be poured continuously, without construction joints. In case a joint is needed to suit the construction conditions, it must be specified in the design.
-
Concrete must be poured continuously in several layers of equal thickness; suitable to the characteristics of the vibrating machine used; and poured in a certain direction for all layers.
-
Pouring concrete using the step method (pouring two or three layers at a time); only done when there is a construction design; and instructions on step concrete pouring technology;
-
-
The allowable stopping time between pouring layers to avoid cold joints must be tested; based on ambient temperature, weather conditions; properties of cement used and other factors to decide.
Note:
- Allowable suspension time for pouring concrete; values in table 18 can be referred to if there are no experimental conditions.
- If the suspension time exceeds the time specified in table 18; the concrete surface must be treated.
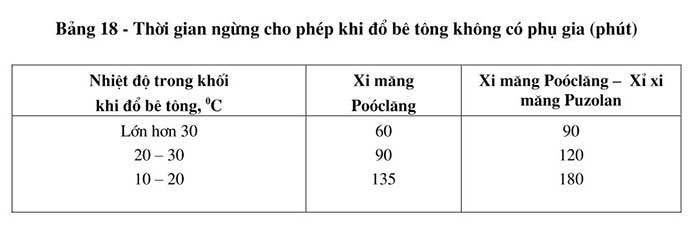
When processing, do the following:
- The strength of the concrete layer below has not reached 25daN/cm2; then do not prepare the surface to pour another layer of concrete;
- The concrete surface has solidified and after 4 hours - 10 hours; use a water jet, iron brush to roughen the concrete surface;
- Before pouring the concrete layer above, the treated concrete surface must be cleaned; dry the water and spread a layer of yellow sand cement mortar 2cm - 3cm thick.
The time to remove the formwork must be based on the achieved strength of the concrete; at the same time, consider the ability to control thermal cracks. Avoid removing the formwork when there is a temperature difference between the concrete block and the ambient temperature. Do not remove the formwork when there is a cold wind. When the temperature inside the concrete and the ambient temperature differ by more than 150ºC - 200ºC; there must be a protective coating on the concrete surface after removing the formwork.
Large block structures without reinforcement; or with little reinforcement can add more rock to reduce the amount of cement; limit the temperature of the poured block; but must ensure the quality according to design requirements.
When constructing concrete with additional rubble, the following regulations must be ensured:
-
The smallest side dimension of the large block structure filled with rock must be greater than 100cm.
-
The largest size of the rubble shall not be larger than 1/3 of the smallest size of the poured mass. Flat diamond-shaped stones shall not be used. The strength of the rubble shall not be lower than the strength of the coarse aggregate in the concrete;
-
- The stones are arranged sparsely and evenly in the concrete block on all sides with a distance of not less than 30cm. The concrete in the tensile zone must not be filled with rubble;
- When pouring concrete with rubble in hot weather; it is necessary to have appropriate measures to reduce the temperature of the rubble; so that the rubble has a temperature similar to the temperature of the concrete mixture immediately after mixing.
Mass Concrete Curing
-
The main task of mass concrete maintenance is to control the temperature difference between the concrete surface and the interior of the concrete block to limit thermal cracking. This maintenance must be based on actual conditions and apply the following measures:
-
Conduct heat from inside the concrete block to the outside by pipes with low temperature water or cold air;
-
Cover the concrete surface to keep the temperature of the concrete block uniform from inside to outside;
-
Do not remove the formwork before seven days.
-
5.2 Concrete work in hot weather and during the rainy season
Concrete construction in hot weather is carried out when the ambient temperature is higher than 300ºC. It is necessary to apply preventive measures; and appropriate treatment for materials, mixing, pouring, compacting; and concrete curing processes to avoid damaging the quality of concrete due to high ambient temperatures.
The temperature of the concrete mixture from the mixer; should be controlled to not be greater than 300C and when pouring not to be greater than 350ºC.
The control of the temperature of the concrete mixture can be based on actual conditions to apply as follows:
- Use cool water to lower the temperature of large aggregates before mixing; use cool water to mix and maintain concrete;
- Construction equipment, vehicles, sand and rock yards, mixing areas and concrete pouring areas must be shaded from the sun;
- Use low-heat cement;
- Use plasticizers with properties suitable for high temperature environments;
- Pour concrete at night or early in the morning; and concrete should not be constructed on days with temperatures above 350ºC.
When performing large-scale concrete work in hot weather, the following requirements must be met:
- There must be drainage measures for sand and rock yards, transport routes, mixing areas and concrete pouring areas;
- Strengthen the testing work to determine the moisture content of aggregates to promptly adjust the amount of mixing water; ensure that the water/cement ratio remains the same according to the selected ingredients;
- There must be a roof over the pouring area when carrying out concrete construction in the rain.
5.3 Concrete work construction with sliding formwork
The process of constructing concrete using sliding formwork is carried out according to the following regulations:
- Pour concrete to create a foot before sliding with a height of 70cm - 80cm, divided into two layers as follows:
- The first layer is poured into the formwork with a height of 35cm - 40cm;
- The second layer is poured next, when the first layer has been poured and compacted on the entire formwork but the concrete has not yet set.
- After the first lifting step, the pouring and sliding process is carried out continuously. At this time, each layer of concrete is poured with a height suitable for the construction measures.
- The formwork lifting is carried out periodically according to the sliding speed; determined in the construction organization design; but it must be ensured that when sliding the concrete batch, the concrete strength has reached 15N/cm2 - 25N/cm2.
- Check the balance of the working floor; the error of the axis center and the verticality of the sliding formwork; carried out with appropriate equipment, means and measures; to ensure technical requirements.
- The concrete surface must be kept moist according to the maintenance regime of TCVN 5592: 1991.
6. Concrete surface finishing
In all cases, the concrete surface must be finished to meet the requirements of quality; flatness and uniformity of color according to the design regulations.
Concrete surface finishing is divided into 2 levels:
- Normal finishing.
- High-level finishing.
Regular finishing:
- After removing the formwork, the concrete surface must be repaired and finished; to ensure smoothness and uniformity of color. The roughness of the concrete surface when measured closely with a 2m ruler must not exceed 7mm.
High-level finishing requires smoothness when tested with a 2m ruler; the roughness must not exceed 5mm and must ensure uniformity and color.
Note:
- The finished concrete surface state here is the structure where the concrete surface does not deviate or does not cover the surface.
- The normal finishing of the concrete surface can be done by many different methods; depending on the level of defect and the nature of the structure. When repairing defects such as pitting, scratches, exposed steel, cracks, etc., it can be done by traditional methods; (plastering, patching, cement mortar spraying, chiseling and smoothing the surface, etc.). When creating uniformity in color, it is important to pay attention to mixing materials; to repair surface defects.
- High-grade finishes are usually done by machine grinding; or by hand depending on the scale, surface area of the structure; and according to design regulations.
6. Inspection and acceptance of concrete work
6.1 Concrete work inspection
The quality inspection of monolithic concrete works includes the following stages: erection of formwork, scaffolding, reinforcement, manufacture of concrete mixture; and tolerances of structures in the project.
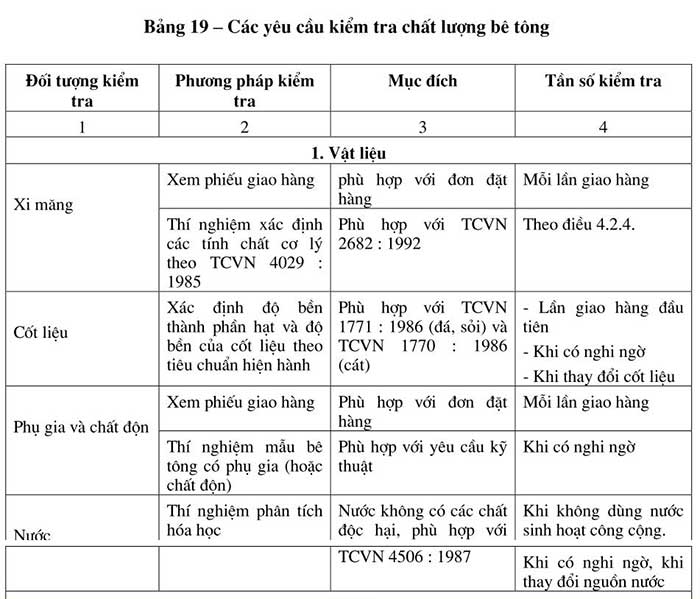
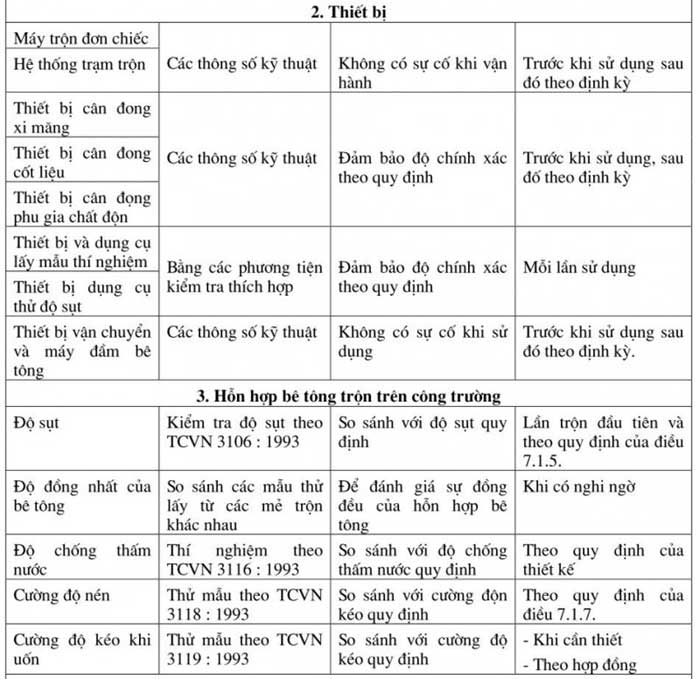
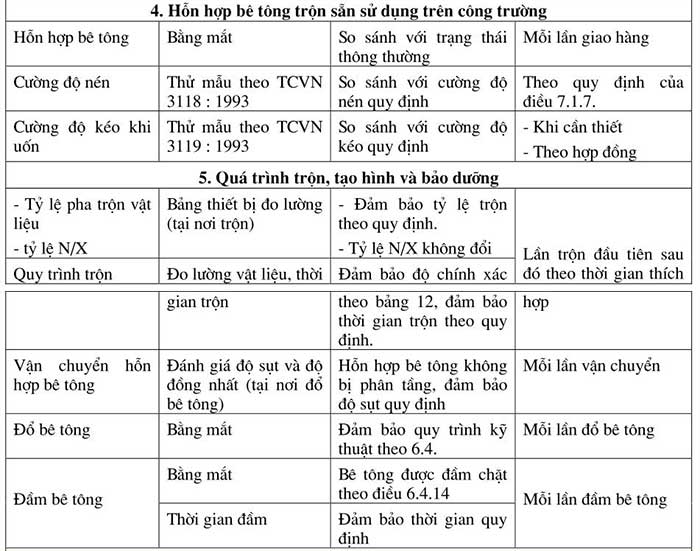
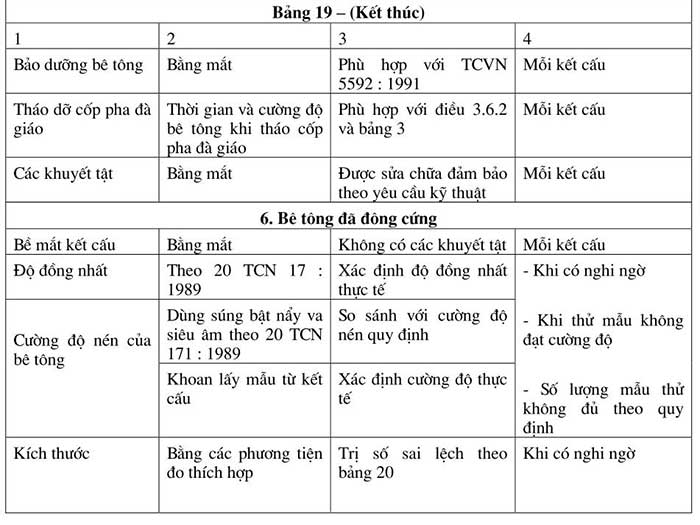
Concrete quality inspection includes inspection of materials, equipment; production process, properties of hardened concrete mixture. These inspection requirements are listed in Table 19.
The slump of concrete mixture is inspected at the site according to the following regulations:
- For concrete mixed at the site, it is necessary to check immediately after mixing the first batch of concrete.
- For ready-mixed concrete at concrete mixing stations (commercial concrete); it is necessary to check each delivery at the concrete pouring site.
- When mixing concrete in weather conditions; and the material moisture is stable, check once per shift.
- When there is a change in the type and moisture of the material as well as when changing the concrete mix composition; it is necessary to check immediately on the first batch; then check again at least once per shift.
Concrete strength test samples are taken at the concrete pouring site; and are kept moist according to TCVN 3105: 1993.
The concrete strength test samples are taken in groups; each group consists of three samples taken at the same time and in the same place; according to the regulations of TCVN 3105: 1993. The standard sample size is 150mm x 150mm. The number of sample groups is specified by mass as follows:
- For large concrete blocks, take one sample group for every 500m3 when the volume of concrete in a poured volume is greater than 1000m3 and one sample group for every 250m3; when the volume of concrete in a poured volume is less than 1000m3;
- For large foundations, take one sample group for every 100m3 of concrete; but not less than one sample group for a foundation block;
- For concrete foundations of machine bases with a pouring volume greater than 50m3, take one sample group; but still take one sample group when the volume is less than 50m3;
- For frames and foundation structures (columns, beams, slabs, arches, etc.), take one sample group for every 20m3 of concrete...;
- In case of pouring concrete for single structures; with a smaller volume, when necessary, take one sample group;
- For concrete foundations, road surfaces (car roads, runways, etc.); take one sample group for every 200m3 of concrete; but if the concrete volume is less than 200m3, a sample set must still be taken;
- To check the water resistance of concrete; take a sample set for every 500m3, but if the concrete volume is less, a sample set must still be taken.
The concrete strength in the construction after testing at 28 days; by pressing samples cast at the site is considered to meet the design requirements; when the average value of each group of samples; is not less than the design grade; and no sample in the group of samples has a strength below 85% of the design grade.
6.2 Acceptance of concrete work
Concrete acceptance work is conducted on site and must have the following complete documents:
- Quality of steel reinforcement work (according to the acceptance report before pouring concrete);
- Concrete quality (through sample testing results and visual observation at the site);
- Size, shape, location of the structure; pre-installed details, expansion joints compared to the design;
- As-built drawings of each type of structure;
- Drawings allowing changes to details and components in the design;
- Results of concrete strength testing on test samples; and quality testing results of other materials, if any;
- Minutes of steel reinforcement and formwork acceptance before pouring concrete;
- Minutes of foundation acceptance;
- Minutes of intermediate acceptance of structural components;
- Construction diary.
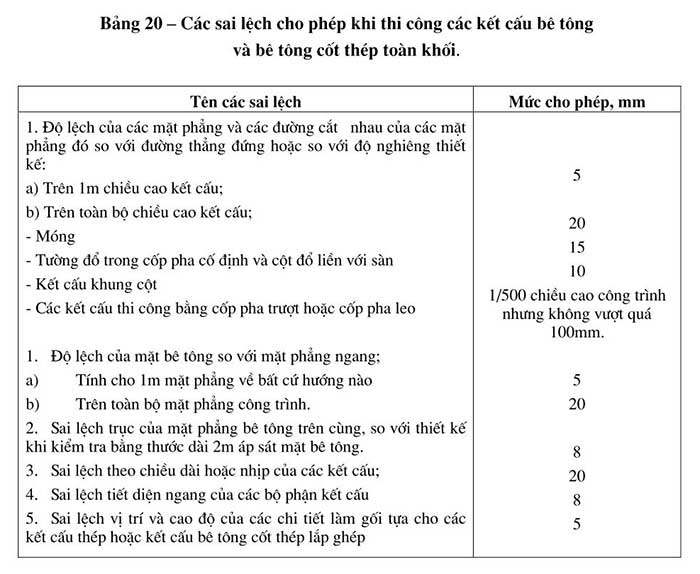
Tolerance allowed.
-
The permissible deviations in size and position of concrete structures; and monolithic reinforced concrete compared to the design; shall not exceed the values given in Table 20. These deviations are determined according to measurement methods using specialized equipment and tools.
7. Introducing a reputable design & construction consulting service provider
The importance of construction units is undeniable, their reputation will ensure the quality and aesthetics of your project. Currently, there are many units providing design and construction services to meet the increasing construction needs in our country. Therefore, finding a reputable unit is not easy and requires you to spend time researching. In the selection process, you need to research carefully and ensure that the accompanying unit must have high expertise, many years of experience, have a clearly signed contract, transparent costs,... To help customers save time searching, Hung Nghiep Phu Construction Investment Co., Ltd. is confident that it will be the best choice for you.

Hung Nghiep Phu Construction Investment Co., Ltd. with the mission of providing the best solutions and services, building a prosperous community with customers, Hung Nghiep Phu is gradually affirming its brand through sincere cooperation, with a leadership team with ethical capacity, creativity, high expertise and strategic vision. Hung Nghiep Phu owns a team of skilled, highly qualified employees who will bring customers the best quality technology.
Hung Nghiep Phu Construction Investment Co., Ltd. - specializes in constructing civil and industrial works. We look forward to accompanying customers in construction projects as well as continuous procedures such as planning diagrams, applying for construction permits, completing procedures, applying for fire prevention and fighting certificates, ... If you have any questions or are in need of design, completing procedures, please contact us immediately for free consultation!
>>> See more:
_____________________
THÔNG TIN LIÊN HỆ:
![]() Facebook: Công ty TNHH Đầu tư Xây dựng Hưng Nghiệp Phú (興業富)
Facebook: Công ty TNHH Đầu tư Xây dựng Hưng Nghiệp Phú (興業富)
![]() Đường dây nóng: 1800.3368 (Miễn phí)
Đường dây nóng: 1800.3368 (Miễn phí)
![]() Trang web: xaydunghunnghiepphu.com
Trang web: xaydunghunnghiepphu.com
![]() Gmail: kinhdoanh01@xaydunghungnghiepphu.com
Gmail: kinhdoanh01@xaydunghungnghiepphu.com
![]() Địa chỉ: Số 2034D, tổ 22, KP Phước Thái, P. Thái Hòa, TP.Tân Uyên, Tỉnh Bình Dương
Địa chỉ: Số 2034D, tổ 22, KP Phước Thái, P. Thái Hòa, TP.Tân Uyên, Tỉnh Bình Dương
------
Nguồn: Tổng hợp từ Internet